Cardio vs. Weight Lifting - Which is Better?
I get asked all the time if we should be spending our time on cardio or resistance training. Is one better than the other? Will lifting weights make you bulky? Does doing cardio actually hurt your metabolism?
I want to start by saying that all exercise “counts” and it is important to do what you like. If you like cardio, great! If you enjoy lifting weights, awesome! I never want to discourage people from moving their bodies in ways that feel good. That said, there are some differences between cardio and resistance training that I want to break down.
Table of contents:
What is cardio?
Cardiovascular exercise (referred to as “cardio” or aerobic exercise) is movement that involves training your heart. Examples of cardio include:
Walking, jogging, and running
Cycling
Swimming
Jumping rope
Rowing
Dancing
Rollerblading
Boxing
Benefits of cardio
Cardiovascular exercise can do more than just strengthen your heart. Cardio may also help with:
Improved circulation
Increased energy
Improved sleep
Blood sugar management
Lowering blood pressure and cholesterol
Reducing stress
What is weight lifting?
Weight lifting (also called resistance training or strength training) involves the use of resistance to build strength, muscle size, and anaerobic endurance. Examples of weight lifting include:
Free weights - dumbbells, barbells, kettlebells
Weight machines
Resistance bands
Suspension equipment
Medicine balls and sand bags
Bodyweight exercise
Benefits of weight lifting
Resistance training can serve many physical and mental health benefits, including:
Improved muscle and bone strength
Injury prevention
Maintaining flexibility and balance
Improved sleep
Improved self-esteem and mood
Prevention and management of chronic conditions
Does cardio or weight lifting burn more calories?
@dietitianhannah #stitch with @kerrimercuryatlaw using weight as a motivator actually tends to be pretty demotivating #dietitianhannah #dietitiansoftiktok #joyfulmovement #intuitiveeating #intuitiveexercise #antidietdietitian #nondietdietitian #haes #dietculture #fitnessculture ♬ original sound - Dietitian Hannah
People often consider how many calories are burned during an exercise session. There is a large focus on using exercise as a means of losing weight, but as mentioned above, there are so many benefits of exercise (both cardio and resistance training) that go beyond calorie burning and weight management.
That said, the amount of calories burned depends on the type of exercise, the duration, and the intensity. We also have to consider an individual’s body size and other metabolic factors. For example, an individual that weighs 200 pounds will generally burn more calories during the same workout than someone that weighs 150 pounds.
In terms of exercise type, a cardio workout will generally burn more calories than a weight lifting session of the same duration. When our heart rate increases during cardiovascular exercise, we start to burn more calories than we would at rest. However, the calories you burn during a workout should not be the only factor considered.
Weight training will result in burning more calories at rest
While you may burn more calories during a cardio workout, weigh lifting may help you to burn more calories at rest. Consistent weight training will help to build muscle. And muscle mass is much more metabolically active than fat mass, meaning that it requires more calories that function that adipose tissue does. In other words, when we lift weights and build muscle, we burn more calories even when we are just chilling on the couch compared to how many we burned with less muscle on our body.
And no, lifting weights will not make you bulky. If you are a biological female reading this, you do not have the necessary hormones to make you “bulky”.
Am I saying that you should never do any aerobic exercise? Nope, of course not. Our heart health is important to. What I am saying is that you do not need to spend hours on the treadmill anymore. In fact, I advise against it unless you truly do enjoy that.
Don’t obsess over the number of calories burned during exercise
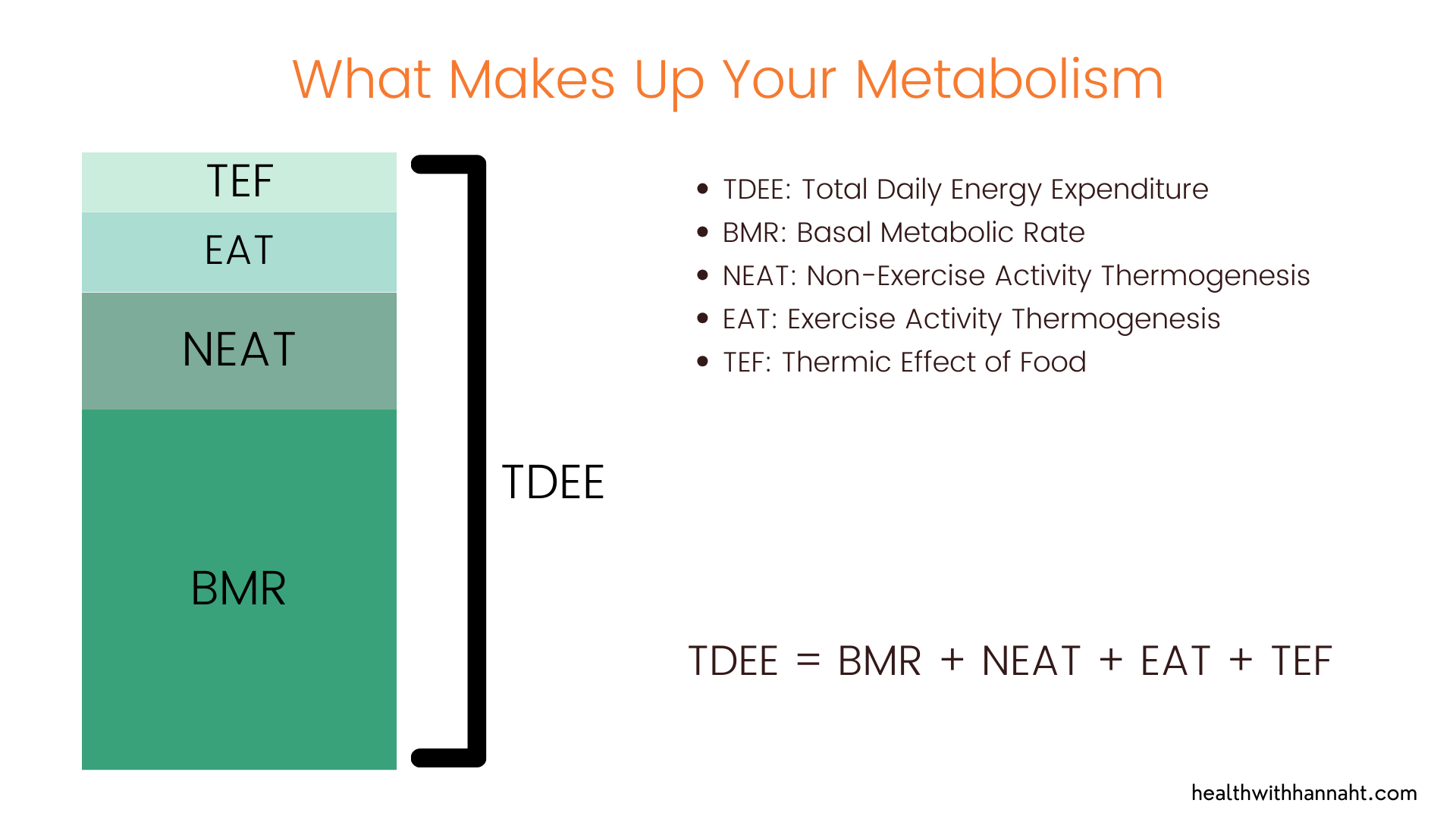
I also couldn’t write this blog without writing about the hyper-fixation that people have on the calories that they burn during workouts. Not only are fitness trackers pretty inaccurate, but the calories that we burn during exercise only contribute about 10% of our total calories burned for the entire day. EAT (exercise activity thermogenesis) plays a small role in our metabolism compared to our basal metabolic rate (BMR) and our non-exercise activity thermogenesis (NEAT).
Exercise alone plays a small role on overall calorie burn. So rather than focusing on calories burned during your workout, perhaps focus on how you can increase your BMR and NEAT. Instead of just eating less and exercising more, we want to learn how to increase our basal metabolic rate so that our body actually needs more calories to function optimally. The best way to increase your BMR? Lift heavy weights and grow those muscles!
How to choose the best exercise for you
At the end of the day, the best exercise to do is whatever you enjoy. Because if you enjoy it, you are more likely to actually do it.
I generally recommend a variation of both cardiovascular exercise along with resistance training. This can be incorporated in so many ways. For me, it involves walking my dog most days along with lifting weights in my garage.
It is important to make movement fun in order to cultivate a positive relationship with exercise. If you’re looking for more guidance on finding your version of joyful movement, check out this post.
Bottom line - is cardio or weight lifting better?
Cardio is beneficial for improving heart health and it can help you to burn calories by increasing your heart rate. However, weight lifting will help you to build muscle mass and improve your resting metabolic rate so you burn more calories day to day.
My recommendation as a dietitian and personal trainer? Do a bit of both!